Vacuum circuit breakers are key components in electrical systems that interrupt current flow and protect circuits from damage caused by overloads or short circuits. Among the various types of circuit breakers, vacuum circuit breakers (VCBs) are widely used in medium and high voltage applications due to their reliability, long service life, and excellent arc extinguishing capabilities.
This article explores the functions of vacuum circuit breakers, their different types including indoor high voltage load switches, indoor high voltage vacuum circuit breakers, and indoor high voltage disconnectors, and key considerations for selecting the right number of poles (3P/4P) for vacuum circuit breakers.
Vacuum circuit breaker are primarily used for:
1. Circuit protection – Safely interrupting current flow during a fault (overload or short circuit).
2. Arc extinguishing – Using vacuum to extinguish arcs and prevent contact damage.
3. Load switching – Enables safe switching of high voltage circuits to avoid arc hazards.
4. Isolation – Provides visible circuit break for maintenance (as indicated by disconnector).

Common applications include:
Distribution networks
Industrial plants
Renewable energy systems (solar/wind farms)
Railway electrification
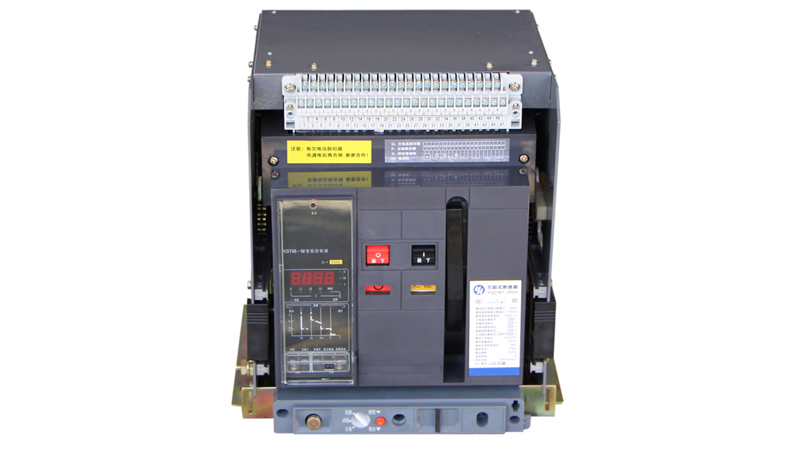
1. Vacuum circuit breaker (VCB)
Uses vacuum as the arc extinguishing medium.
For indoor high voltage applications (up to 40.5 kV).
Low maintenance and long service life.
2. Indoor high voltage load switch
Designed to switch loads (but not fault currents).
Often used in conjunction with circuit breakers for increased safety.
Commonly used in substations and industrial power systems.
Provides maintenance isolation (no load breaking capability).
Must be used in conjunction with circuit breakers for full protection.
Ensure visible opening clearance for safety.
When choosing between 3-pole (3P) and 4-pole (4P) vacuum circuit breakers, consider the following factors:
| Factors | 3-pole (3P) | 4-pole (4P) |
| Application | Standard three-phase systems | Systems requiring neutral disconnection |
| Neutral handling | Neutral not switched | Neutral switchable/isolated |
| Use cases | Industrial motors, general power distribution | IT systems, sensitive equipment (hospitals, data centers) |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to extra poles |
Unbalanced loads (higher neutral current).
Ground fault protection (for disconnecting the neutral in a fault condition).
IT power systems (neutral isolation is critical).
Balanced three-phase system (no neutral disconnect required).
Cost-sensitive applications (no need to use 4P).
Vacuum circuit breakers play a vital role in electrical safety and efficiency, and various types vacuum circuit breakers, load switches, disconnectors are available to meet different needs. Choosing the right pole configuration (3P/4P) depends on system requirements, neutral handling, and safety standards.
For high-voltage indoor applications, always refer to industry standards (IEC, ANSI) and work with certified suppliers to ensure optimal performance and safety.